Trade Protection Definition Economics
Free trade eliminates tariff while protective trade imposes tariff or duty. Price of foreign.
International Trade Trade Protection Subsidy
Protectionism is the economic policy of restricting imports from other countries through methods such as tariffs on imported goods import quotas and a variety of other government regulationsProponents argue that protectionist policies shield the producers businesses and workers of the import-competing sector in the country from foreign competitors.

Trade protection definition economics. AQA Edexcel OCR IB. The motives for protection The main arguments for protection are. Trade protection is the deliberate attempt to limit imports or promote exports by putting up barriers to trade.
Protectionism represents any attempt to impose restrictions on trade in goods and services. Intervention in international trade involving the imposition of trade barriers intended to limit the quantity of imports and protect the domestic economy from foreign competition. Protectionism involves any attempt by a country to to impose restrictions on the open trade in goods and services.
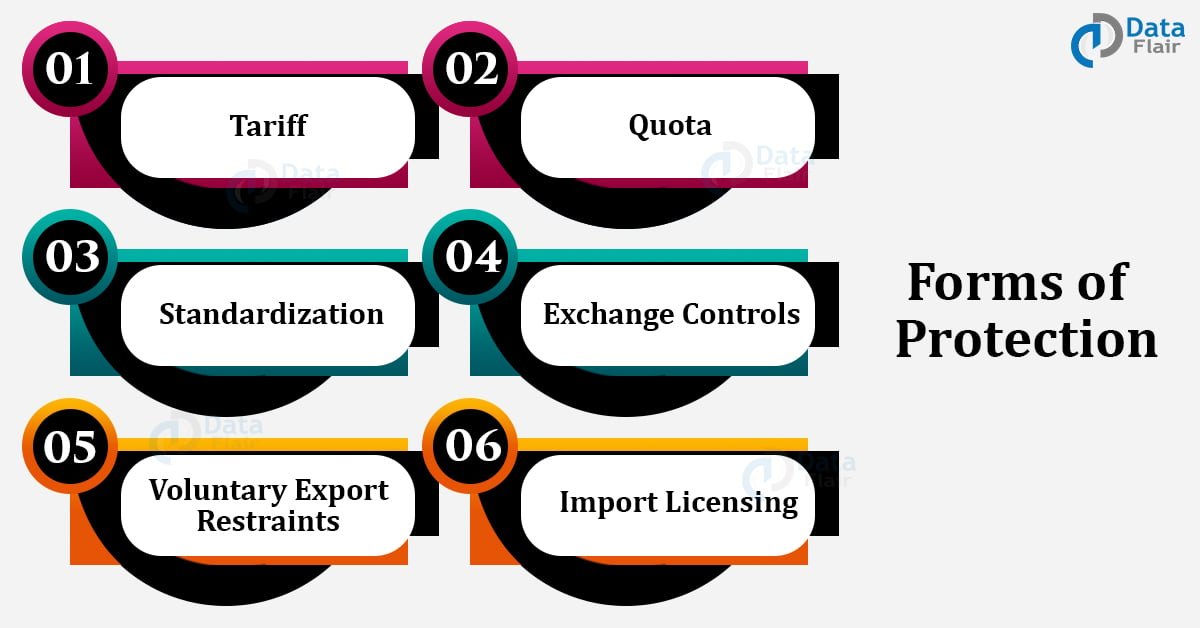
Producers against foreign producers in a particular industry by means of raisin g the. A quota or protectionism is a government-imposed trade restriction limiting the number or value of goods a nation imports or exports. Tariffs are taxes that are placed on imported goods.
10 Examples of Non-Tariff Barriers - revision video. ARGUMENTS FOR PROTECTION Protecting the Economy from low-cost labour Counter Argument for Free Trade If we protect the economy from low-cost labour it will mean that consumers pay higher prices than they should. A nation may adopt protectionist measures in order to protect domestic jobs industry national security and to protect the consumer.
Bergson Samuelson Arrow et al. But even this argument is not convincing as protection cannot maintain high employment indefinitely through export surplus. When tariffs duties and quotas are imposed to restrict the inflow of imports then we have protected trade.
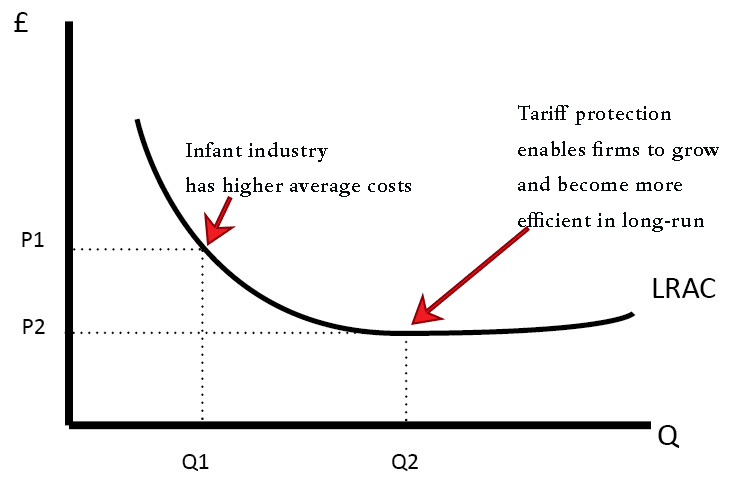
Blooming Glory A countrys protectionism will mean the protection of home industries or infant industries until they are large enough to achieve economies of scale and strong enough to. Definition of Trade Protection Govt. A discussion of the political economy of trade policy can usefully begin by placing the subject in the framework established by Bergson and Samuelson for analyzing social welfare.
Foreign trade of a country may be free or restricted. Import tariffs basic analysis - revision video. Free trade differs from other forms such as trade policy where the allocation of goods and services amongst trading countries are determined by artificial prices that may or may not reflect the true nature of supply and demand.
The main aim of protectionism is to cushion domestic businesses and industries from overseas competition and prevent the outcome resulting solely from the interplay of free market forces of supply and demand. Protectionism policy of protecting domestic industries against foreign competition by means of tariffs subsidies import quotas or other restrictions or handicaps placed on the imports of foreign competitors. Baldwin 101 Welfare Economics.
By improving the balance of trade it can increase employment and income provided the other countries do no retaliate. Despite the arguments in favour of free trade and increasing trade openness protectionism is still widely practiced. Production in a protected economy would take place at an inefficient level.
Protection can of course increase employment in another way. In the international trade context the subsidy is given to domestic producers to increase their international competitiveness. Protectionism is the sum of government trade policies intended to assis t domestic.
Trade GATT was signed with objectives of encouraging international trade and reducing tariff as possible. Ten examples of non-tariff barriers - revision video. Protect sunrise industries Barriers to.
There are many types of protectionism such as subsidies restrictions on FDI exchange rate. Trade protection - the imposition of duties or quotas on imports in order to protect domestic industry against foreign competition. 31 International Trade Trade Protection.
By protection we mean restricted trade. Subsidy government payment to producers attempting to lower the price of produce and increase quantity produced encourage production. Protectionist policies have been implemented by many countries despite the fact that virtually all mainstream economists agree that the world economy generally benefits.
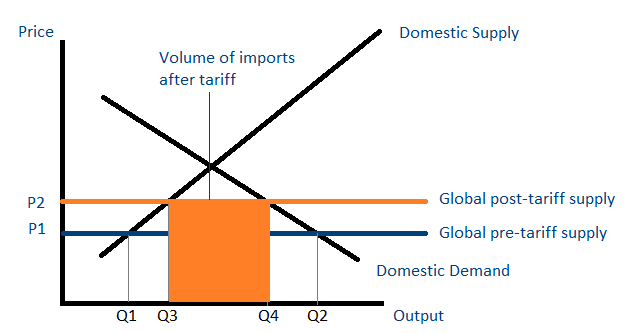
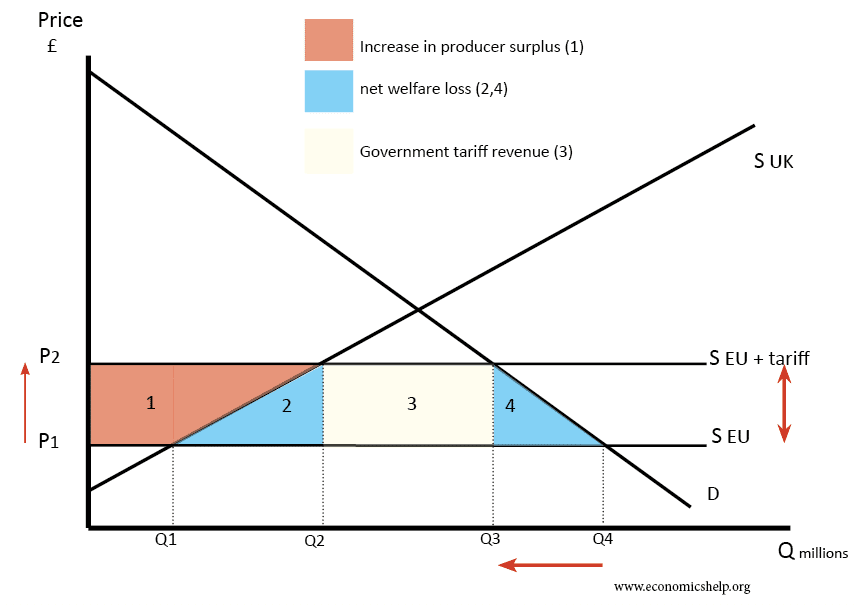
The diagram above is a diagram for the UK importing chicken wings. Tariff a tax on imports with an attempt to restrict imports possibly raise revenue for the government however during an exam check the context the term is used in and tweak the definition to fit Consider the tariff diagram below. 31 International Trade Trade Protection.
Protectionism Definition Types Advantages And Disadvantages
/anti-free-trade-postcard-526930930-5c054e4f46e0fb000123437b.jpg)
Understanding The Pros And Cons Of Protectionism

Arguments For And Against Protectionist Policy Boundless Economics
International Trade Trade Protection Tariff

Trade Barriers Intelligent Economist
/TariffsAffectPrices1_2-e3858c9eddb649a8b3ffc70af1f9938b.png)
The Basics Of Tariffs And Trade Barriers
Infant Industry Argument Economics Help

Protectionism Definition 6 Types Advantages Disadvantages Boycewire
The Effects Of Protectionism Economics Help

Protectionism Definition Examples Facts Britannica
International Trade Trade Protection Quota
/anti-free-trade-postcard-526930930-5c054e4f46e0fb000123437b.jpg)
Understanding The Pros And Cons Of Protectionism
Protectionism Types Advantages And Limitations Dataflair
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TariffsAffectPrices1_2-e3858c9eddb649a8b3ffc70af1f9938b.png)
The Basics Of Tariffs And Trade Barriers

28 Key Pros Cons Of Protectionism E C
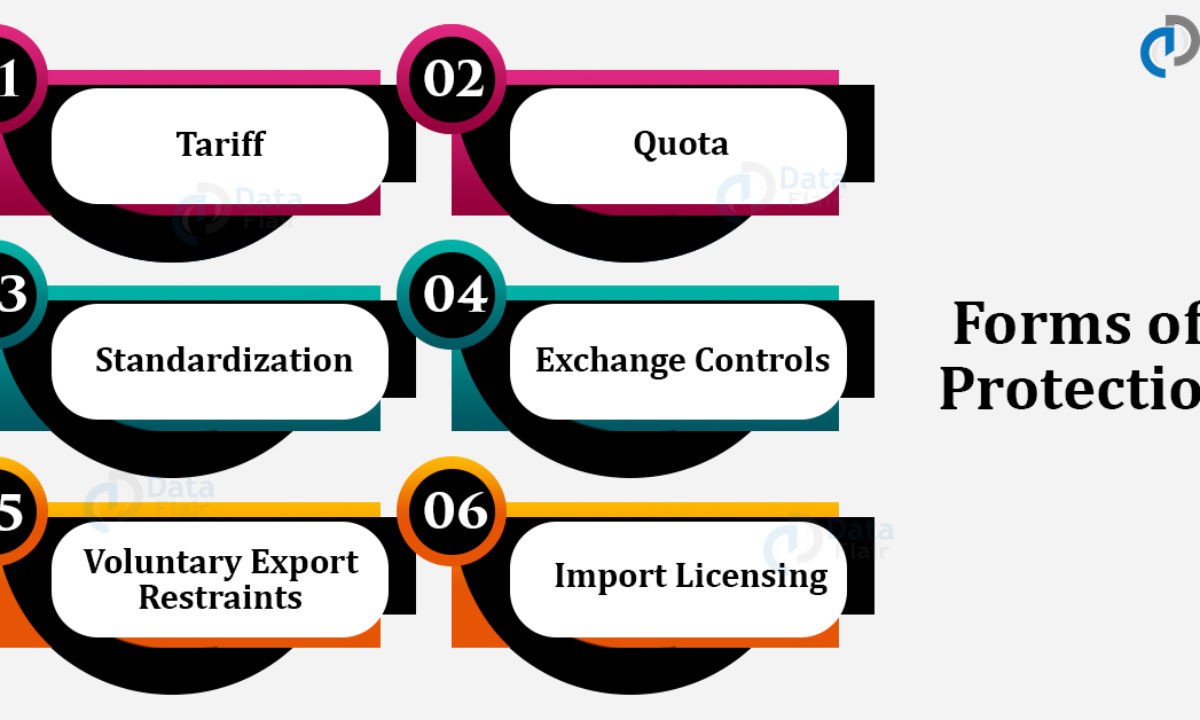
Protectionism Types Advantages And Limitations Dataflair
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/trade-wars-definition-how-it-affects-you-4159973_color-bf45e3ae6bad40e09e5485c8f6fa7c75.png)
Post a Comment for "Trade Protection Definition Economics"